In today’s digital landscape, where privacy and data security are paramount, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have become a go-to solution for individuals and businesses alike. VPNs create a secure and encrypted connection between a user’s device and the internet, safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring online anonymity. However, VPN providers often face the challenge of limited IP addresses, which can hinder their ability to offer seamless services. To overcome this hurdle, Network Address Translation (NAT) steps in as a crucial component in the VPN ecosystem.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the depths of NAT, explore its role in VPNs, and shed light on how it effectively addresses the challenges of IP sharing.
Understanding Network Address Translation (NAT):
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a technology that enables multiple devices within a private network to share a single public IP address. Acting as a bridge between the private network and the public internet, NAT dynamically translates the private IP addresses of devices into a single public IP address. This translation allows devices within the private network to communicate seamlessly with external servers and services on the internet.
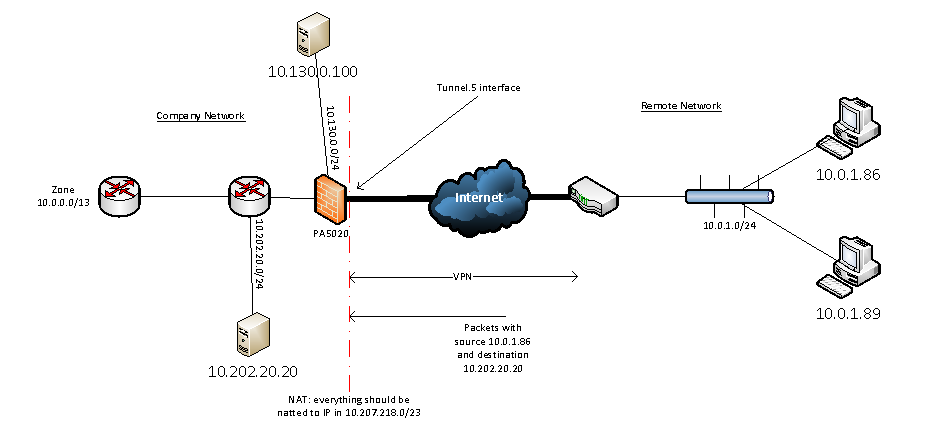
NAT in VPNs: Addressing IP Sharing Challenges:
When it comes to VPNs, NAT plays a pivotal role in optimizing IP address utilization and overcoming the challenges of IP sharing. Let’s dive deeper into the specific ways NAT enhances the functionality of VPNs:
- IP Address Conservation:
With the growing scarcity of IP addresses, NAT offers a valuable solution by employing a technique called Port Address Translation (PAT). Instead of assigning each device a unique public IP address, NAT assigns each device a unique port number on the public IP address. This innovative approach enables multiple devices to share the same public IP address, significantly reducing the number of public IP addresses required by the VPN provider. By conserving IP addresses in this manner, VPN providers can efficiently cater to a larger user base while minimizing resource consumption.
- Enhanced Security:
In the realm of VPNs, security is paramount. NAT provides an additional layer of protection by acting as a mediator between the private network and the internet. By doing so, it effectively masks the internal IP addresses of devices from external entities, adding an extra level of anonymity and shielding devices within the private network from potential attackers. This enhanced security aspect distinguishes NAT-enabled VPNs as a robust choice for safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring online privacy.
- IP Address Flexibility:
Flexibility is essential for VPN providers to adapt to the dynamic nature of user demands. NAT offers a dynamic IP address assignment capability, allowing VPN providers to allocate private IP addresses to devices within the private network as needed. This eliminates the need for a large pool of static public IP addresses and provides greater scalability. VPN providers can seamlessly accommodate a growing user base without worrying about running out of available IP addresses. This flexibility enables VPN services to be more agile and responsive to changing user needs.
- Seamless Integration:
Incorporating VPNs into existing networks and infrastructure can be a complex task. However, NAT simplifies this process by facilitating seamless integration. Since many organizations already utilize NAT for their internal networks, VPN providers can leverage this existing infrastructure without the need for extensive modifications. This integration enables VPN clients to connect effortlessly to the VPN server using the NAT-enabled network, streamlining the deployment and configuration process.
Additional Insights
To further illustrate the practical application of NAT in VPNs, let’s consider a practical example. Imagine a large organization that needs to provide secure remote access to its employees. By implementing a VPN with NAT capabilities, the organization can offer a secure and encrypted connection to all employees using a limited number of public IP addresses. NAT efficiently manages IP address allocation, allowing employees to connect to the company’s private network while maintaining privacy and data security.
Furthermore, NAT also facilitates the establishment of site-to-site VPNs, where multiple remote locations need to connect securely. By utilizing NAT, organizations can create secure connections between their different offices using a single public IP address. This significantly reduces the complexity and costs associated with maintaining a large number of public IP addresses for each location.
Conclusion
In conclusion, NAT plays a vital role in addressing the IP sharing challenges faced by VPN providers. It optimizes IP address utilization, enhances security, provides flexibility in managing IP addresses, and enables seamless integration with existing networks. NAT’s ability to conserve IP addresses through Port Address Translation, coupled with its robust security features, makes it an indispensable component of modern VPN services. As VPNs continue to gain traction as essential tools for privacy and data protection, NAT remains at the forefront, ensuring the efficient and secure operation of these invaluable solutions.